What is Diamond Cut?
Cut is the artistry that transforms a rough stone into a dazzling diamond. While often confused with shape, which defines the diamond's outline, cut is the precise craftsmanship that determines how light interacts with the gem. A diamond's brilliance is maximized through careful attention to its proportions, symmetry, and polish.
-
Fair
This cut prioritizes weight over brilliance. While it reflects light adequately, its sparkle isn't as intense as a diamond with a superior cut.
-
Good
A premium cut that balances maximum size with unparalleled brilliance and clarity. Optimizes light return for a dazzling display.
-
Very Good
Offers superior sparkle compared to many other cuts, while being considerably more affordable than the top-tier option.
-
Ideal
Exquisitely crafted to produce the highest level of brilliance and fire. This exceptional cut ensures maximum light return.
-
Super Ideal
Precision-cut to perfection, these diamonds boast optimal dimensions for maximum light return.
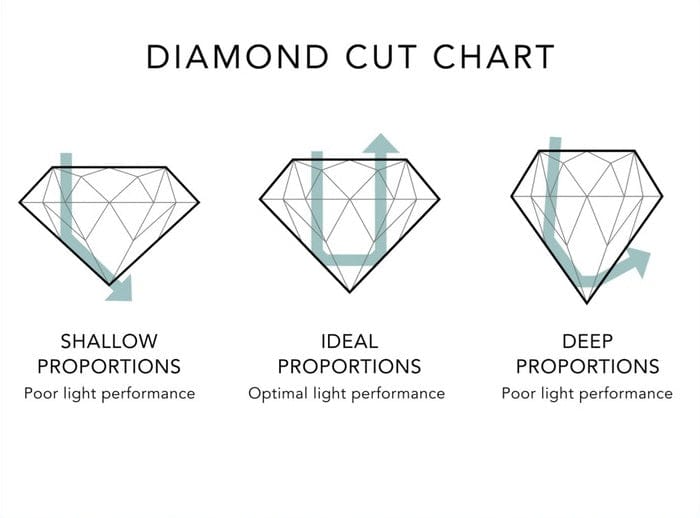
Why is Cut Important?
The cut of a diamond is the key to its brilliance. An expertly crafted diamond maximizes light return, creating the iconic sparkle we associate with these precious stones. Conversely, a poorly cut diamond appears dull and lifeless. Understanding cut is essential for choosing a diamond that truly shines.

How is Diamond Cut Graded?
The GIA has established a comprehensive system for assessing the quality of a diamond's cut. Through in-depth research on how light interacts with round brilliant diamonds, the GIA developed a grading scale that evaluates factors such as a diamond's brilliance, fire, scintillation, proportions, polish, and symmetry. The grades range from Excellent, the highest, to Poor.
Various gem labs have distinct grading systems for diamond cuts. The IGI, for example, includes an "Ideal" grade beyond the GIA's "Excellent." To offer customers a more precise understanding of cut differences and their price implications, TrueSanity uses a comprehensive scale from "Super Ideal" to "Poor." Our grading is aligned with the certifying lab's specifications. Consequently, a GIA "Excellent" diamond could be classified as "Super Ideal" or "Ideal" on our site.
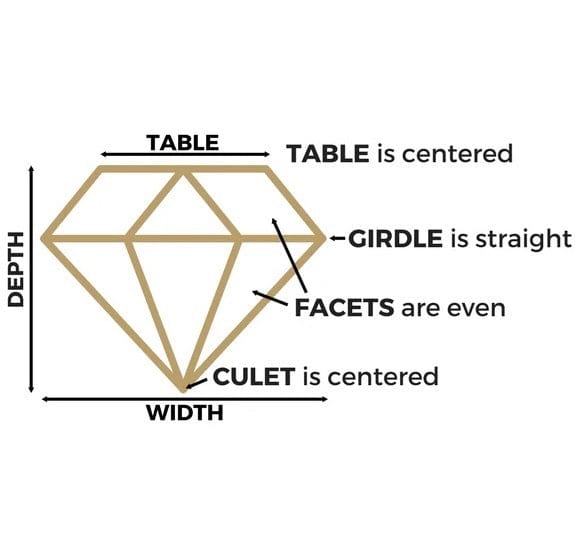
Cut Characteristics of a well-cut diamond
The ratio of a diamond's TABLE, DEPTH, and WIDTH has a large impact on cut grade.
Polish
Polish refers to the quality of a diamond's surface finish. The smoothness of the diamond's exterior, free from imperfections like pits or scratches, determines its polish grade. This grade, ranging from Ideal to Poor, is typically documented on a diamond certificate.
Symmetry
Symmetry refers to the precision of a diamond's shape and the alignment of its facets. It encompasses both the overall outline and the internal arrangement of the facets. Graded from Ideal to Poor, symmetry is a crucial factor in determining a diamond's brilliance and is typically detailed on a diamond certificate.
Proportion
A diamond's proportions, determined by the angles and measurements of its facets, significantly impact its overall appearance. These facets act as tiny mirrors, and their precise arrangement influences how light interacts with the diamond, creating its brilliance and sparkle.
Brilliance
Brilliance is the dazzling white light a diamond reflects. This radiant glow is created as light enters the diamond and bounces off its internal facets. The precision of the cut determines how effectively light is captured and returned, producing a brilliant display.
Fire
Fire is the magical display of rainbow colors that dance within a diamond. This phenomenon occurs when white light enters the stone and is dispersed into its spectral components. To achieve this breathtaking effect, a diamond must be cut with precision. Poorly cut diamonds fail to capture and disperse light effectively, resulting in a less vibrant and colorful display.
Scintillation
Scintillation is the dynamic sparkle of a diamond. As it moves, facets disperse white light into a rainbow of colors, creating shimmering flashes on the surface. These bright bursts contrast dramatically with the darker areas caused by light refracting within the stone, producing an overall dazzling effect.

Cut Grades
Having grasped the essential elements of diamond cut evaluation, let's discover how TrueSanity categorizes diamonds to guide your purchase.
Super Ideal
A Super Ideal cut diamond is a masterpiece of craftsmanship, boasting perfect proportions, flawless polish, and impeccable symmetry - the coveted "Triple Excellent" rating from GIA/IGI. These diamonds exhibit unparalleled brilliance and fire, captivating the eye with their extraordinary sparkle.
Ideal
An Ideal cut diamond adheres closely to perfect proportions, while its polish and symmetry may be slightly less than flawless. Despite this minor difference, the untrained eye will find an Ideal diamond equally stunning as a Super Ideal, provided they share the same color and clarity.
Very Good
A Very Good cut diamond is expertly crafted with proportions that closely approximate the ideal, coupled with excellent to moderate levels of polish and symmetry. These stones offer exceptional brilliance at a more attainable price point.
Good
A Good cut diamond is characterized by minor imperfections in its proportions, resulting in a decent amount of light reflection. However, its brilliance is noticeably less impressive than higher-grade diamonds due to the presence of darker areas within the stone. While offering a more affordable price, the overall sparkle may be compromised.
Fair
A Fair cut diamond lacks the brilliance found in higher-quality stones. Its poor light return is due to dark areas on the crown and within the diamond itself. While more affordable, its diminished sparkle often discourages buyers.
Poor
Diamonds with a Poor cut grade are typically not recommended. Their light return is dramatically reduced due to light leakage, resulting in a dull and lifeless appearance. These stones often have prominent dark areas that diminish their overall beauty. To ensure the highest quality, TrueSanity does not carry diamonds with a Poor cut rating.

Different Types Of Diamond Cuts
Now that we've covered the criteria used to evaluate diamond cut, we'll examine how a diamond's facets are crafted. It's essential to distinguish between a diamond's shape, which is its overall outline, and its cut, which is the artistry of its facets.
Round Brilliant Cuts
The most beloved diamond shape, the round brilliant, is meticulously cut with 57 to 58 facets to maximize its brilliance, fire, and sparkle.
Fancy Cuts
Any diamond shape other than round is classified as a fancy cut.
Modified Brilliant Cuts
A modified brilliant cut is a variation of the classic round diamond shape. Popular examples include pear, marquise, cushion, oval, and heart cuts.
Step Cuts
Step-cut diamonds are characterized by their rectangular facets arranged in a stair-like pattern. Unlike brilliant cuts, they prioritize clarity and elegance over maximum sparkle. Popular step-cut shapes include emerald, asscher, and baguette.
Rose Cuts
Unlike step-cut or brilliant-cut diamonds, rose cuts have a flat base, giving them a lower profile. While this contributes to their unique aesthetic, they offer a softer, less intense sparkle compared to other cuts. Rose cuts can be crafted in various shapes, though round is the most common.
Vintage Cuts
Before advanced technology, diamond cutters prioritized preserving the raw stone's weight over maximizing brilliance. Consequently, older cuts like old mine and euro-cut have larger facets and less sparkle than their contemporary counterparts.

How Does Diamond Cut Impact Price?
A diamond's price is influenced by all four Cs, including its cut. Generally, higher cut grades correlate with higher prices. Finding your ideal diamond often involves balancing your budget with desired qualities. For instance, if brilliance is paramount, you might prioritize cut and adjust expectations for carat, color, or clarity to fit your budget.